Table Of Content

Anagen growth is the active phase in which the hair follicle takes on its onion-like shape and works to produce the hair fiber. The anagen phase can be further broken down into proanagen and metanagen phases. Proanagen sees the follicle proliferating hair progenitor cells and begins the differentiation process.
What role do keratin proteins play in hair structure?
The observed differences in the X-ray diffraction patterns between different individuals can, therefore, most likely be assigned to differences in the molecular composition of the plasma membrane in the cell membrane complex. Differences in the X-ray data between individuals were observed in the wide angle region (WAXS) of the 2-dimensional data in Fig. Figure 7A shows a comparison between individual 3 and 4 to illustrate the effect. For an easy comparison, the original data were cut in half and recombined, such that the left half depicts individual 3, and the right half individual 4. Due to the large length scales involved, the signals from intermediate filaments occur at small scattering vectors, shown in Fig.
In brief: What is the structure of hair and how does it grow?
It allows the other layers of the scalp to slide off over the pericranium. Known also as the epicranial aponeurosis or the galea aponeurotica, this is an important structure within the scalp. It is a thin but tough layer of fibrous tendinous tissue and is the site at which the occipitofrontalis muscle inserts into the tissue of the scalp. The occipital belly gives rise to it, whereas the epicranial aponeurosis inserts into the frontal belly of the occipitofrontalis.
How Our Hair Grows: The Anatomy Of Hair Follicles
Injecting Electrons Jolts 2-D Structure Into New Atomic Pattern - Berkeley Lab - Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (.gov)
Injecting Electrons Jolts 2-D Structure Into New Atomic Pattern - Berkeley Lab.
Posted: Wed, 11 Oct 2017 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Telogen effluvium is when hair roots are pushed into the telogen resting phase. This usually occurs after some stress and can be acute or chronic. The unwanted loss of hair, known as alopecia, is a widespread condition affecting both sexes, occurring in numerous patterns, and classified into non-scarring and scarring (cicatricial) subtypes.
New hair cells then start to multiply at the base of the “empty” hair follicle to form a new hair, and the growth phase of the hair growth cycle starts all over again. As long as new hair cells continue to grow in the hair bulb, the hair continues to grow longer. At any point in time, about 90 percent of a person’s total amount of hair is in this growth phase. The full strand of hair develops from this group of hardened hair cells. Because new hardened cells keep on attaching to the hair from below, it is gradually pushed up out of the skin. In this way, a single hair on your head grows at a rate of about 1 cm per month.
Research leads to new discoveries about structure of human hair - Phys.org
Research leads to new discoveries about structure of human hair.
Posted: Thu, 28 Jan 2016 08:00:00 GMT [source]
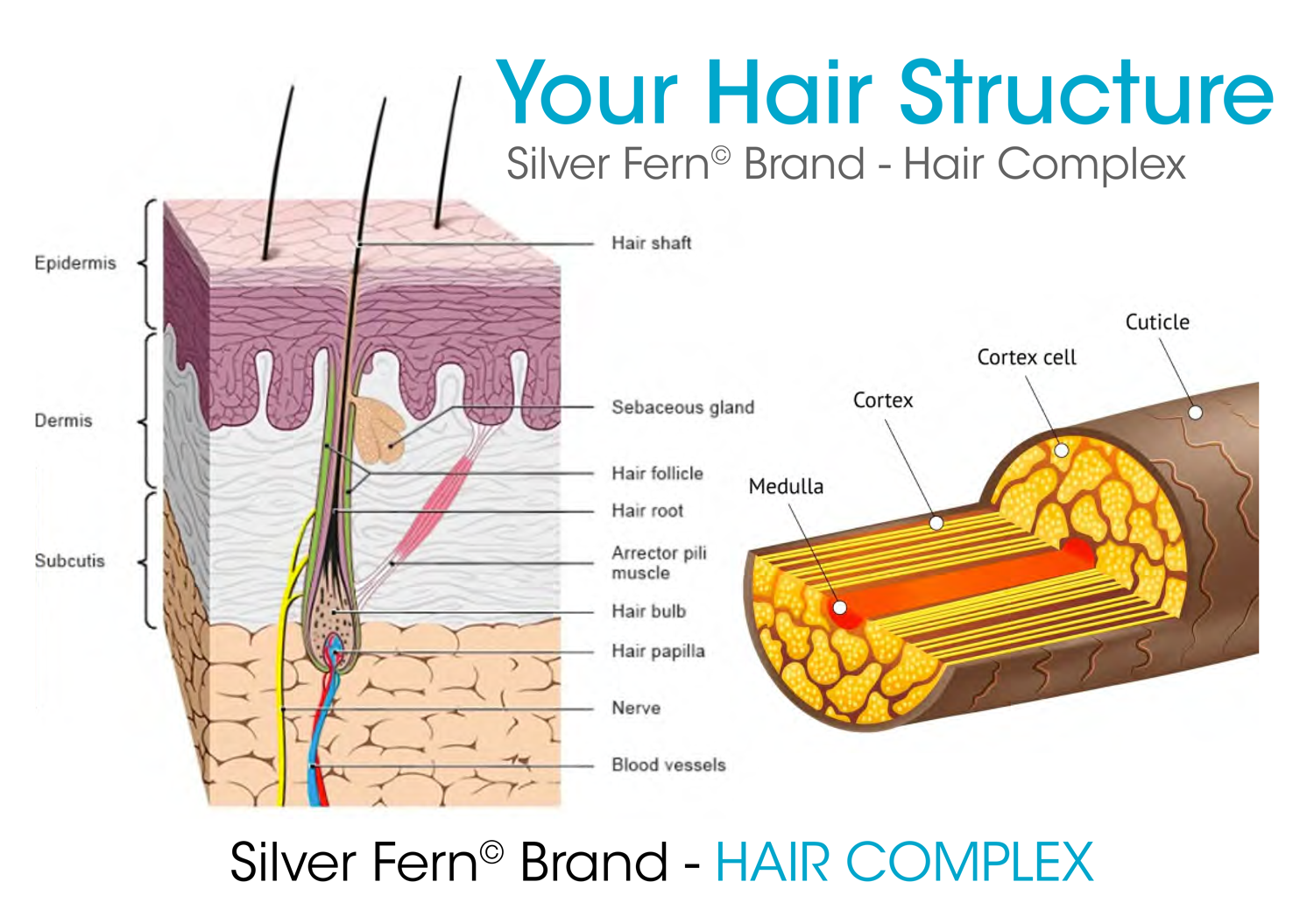
These older cells die and become keratinized in the process. The cross-sectional shape of hair also determines the amount of shine that the hair has. Straighter hair is shinier because sebum from the sebaceous gland can easily travel down the hair. With curly hair, the sebum has trouble traveling down the hair, making it look more dry and dull. The follicle is lined by an inner and outer sheath that protects and molds the growing hair.
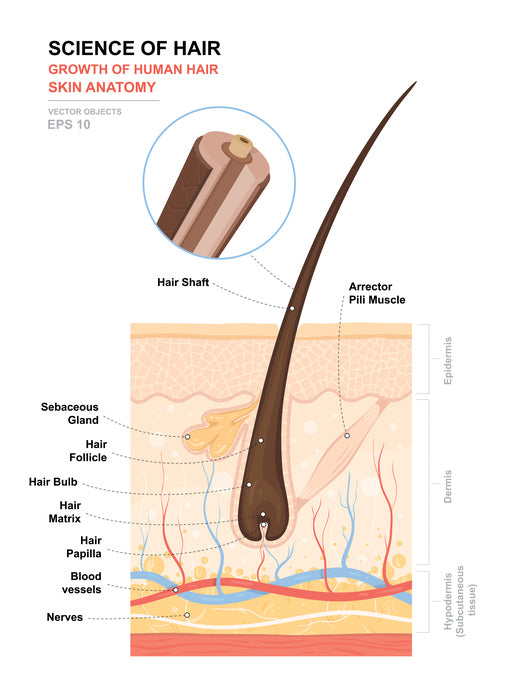
In the precortical matrix, these melanosomes are transferred to the hair shaft keratinocytes and formed a pigmented hair shaft. The hair follicle also contains melanocyte stem cells, which are located in the bulge and in the secondary hair [33–35]. Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis. Strands of hair originate in an epidermal penetration of the dermis called the hair follicle. The hair shaft is the part of the hair not anchored to the follicle, and much of this is exposed at the skin’s surface.
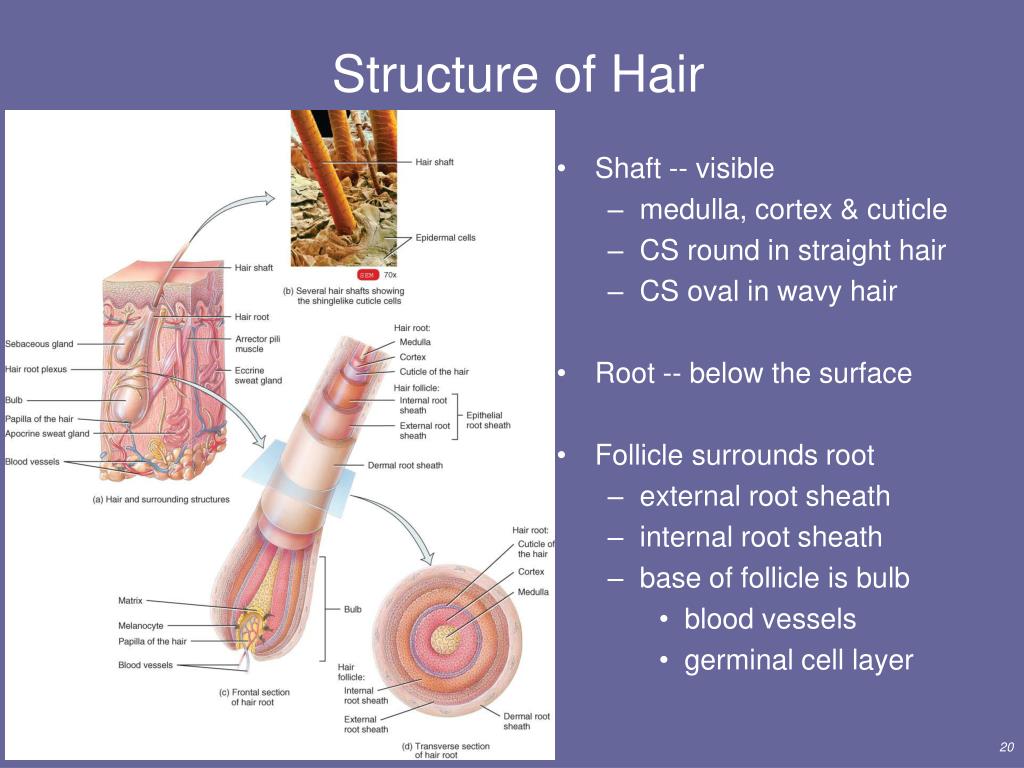
It is the dermal papilla, the cell of which divides and differentiates to give rise to a new hair follicle. As if that wasn't scientific enough, it's the lower part of the hair follicle that has stem cells, Gupta adds. You'll notice the bulb if you were to pull a hair strand from the root. Androgenetic alopecia is the most common presenting hair concern and affects 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States alone. Studies estimate that 70% of men and 40% of women are affected by androgenetic alopecia.
A thorough history, physical exam, hair pull test, daily hair counts, part width, clip tests to examine the hair shaft, hair growth windows, and hair pluck, and trichograms can all be used to diagnose hair disease. Scalp biopsies, hormone studies, and a potassium hydroxide examination for fungi may also need to be performed in certain cases. It is important to diagnose hair disease correctly, as the treatment for hair loss is dependent on the diagnosis. Hair is continually shed and renewed by the operation of alternating cycles of growth, rest, fallout, and renewed growth.
Hair loss can also result from the aging process, or the influence of hormones. The wall of the hair follicle is made of three concentric layers of cells. The cells of the internal root sheath surround the root of the growing hair and extend just up to the hair shaft. The external root sheath, which is an extension of the epidermis, encloses the hair root. It is made of basal cells at the base of the hair root and tends to be more keratinous in the upper regions.
The hair is gradually pushed out of the skin and eventually falls out. The color of the hair is determined by the amount of melanin in the hardened cells. This can vary a lot from person to person, and it changes over the course of a lifetime. The amount of melanin typically decreases as people get older, and more air gets trapped inside the hair – it then loses its color and turns white. Depending on someone’s original hair color and the number of white hairs that grow, the hair on their head then turns gray or white. All natural hair colors are the result of two types of hair pigments.
As its name might suggest, this type of tissue forms a loose connection between the epicranial aponeurosis and the pericranium. This allows the other layers of the scalp to slide of over the pericranium. Loose areolar tissue comprises a network of reticular fibers, elastic tissue, and collagen. Since this is a loose connective tissue, cell types vary beyond fibrocytes and can include plasma cells, mast cells, and adipocytes.
In the direction perpendicular to the hair fibre axis (q‖), there are also two major peaks consistent among all subjects, one narrow peak around 9.5 Å and one broad peak around 4.3 Å. The total scattering profile was well fit by two Lorentzian peak profiles (and a background), whose positions is plotted in Fig. The signals at 5.0 Å and 9.5 Å are in excellent agreement with signals reported from coiled-coil keratin proteins (Pauling & Corey, 1950), as depicted in the Figure. The broad signal at about 4.3 Å present in both directions is due to the ring-like scattering from the lipids in the membrane component.
The bulge area is located in the middle part (also known as the isthmus) of the hair follicle. It contains stem cells that divide and regenerate not only new hair follicles but the sebaceous glands and the epidermis, too. The fourth cell layer of the hair follicle comprises the internal root sheath. This is to leave a space into which sebum can be secreted around the hair.